Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection (RSV)
|
|
Respiratory syncytial virus or RSV, is a common respiratory virus that usually causes mild, cold-like symptoms. Most people recover in a week or two, but RSV can be serious, especially for infants and older adults. RSV is the most common cause of bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lung) and pneumonia (infection of the lungs) in children younger than 1 in the U.S. -CDC
To view the RSV dashboard for the state of Nebraska |
|---|
|
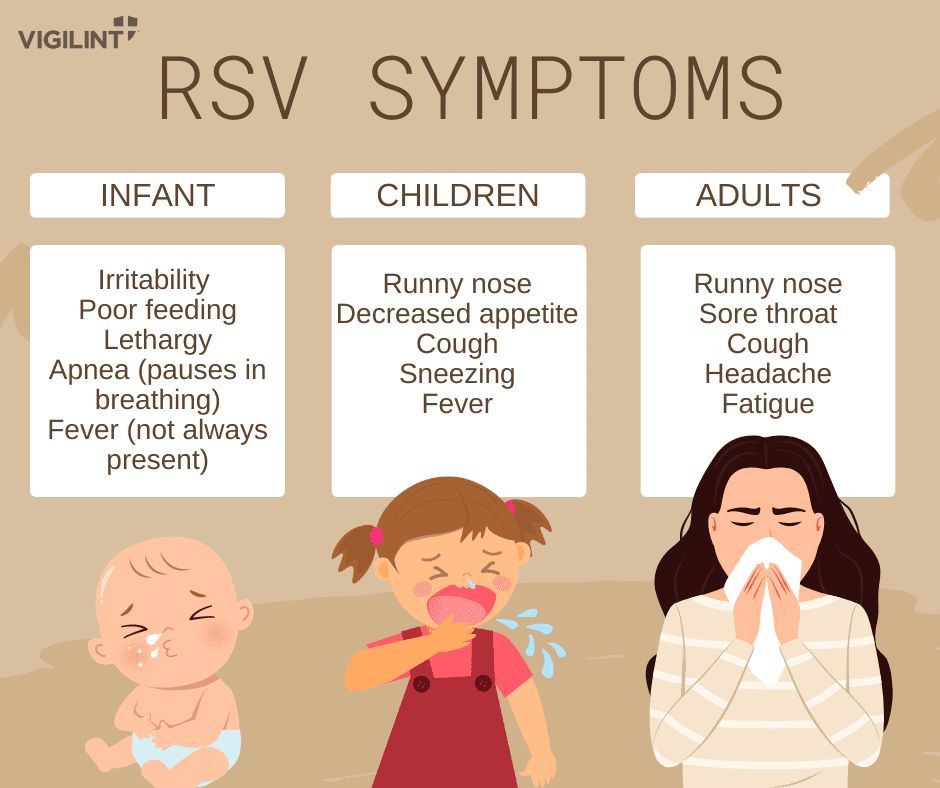
Symptoms and Care Symptoms Runny Nose Decrease in appetite Coughing Sneezing Fever Wheezing Symptoms usually appear in stages and not all at once. Very young infants may only show irritability, decreased activity, and difficulty breathing. Almost all children will have had an RSV infection by their second birthday. Care Steps to relieve symptoms:
|
Preventing RSV Take these steps to prevent the spread of RSV.
|
Transmission RSV spreads when
Individuals who are infected with RSV are usually contagious for 3 to 8 days after symptoms and may be contagious up to 48 hours prior to symptoms. RSV can survive for many hours on hard surfaces such as tables and cribs. People at higher risk for RSV are:
|
 |
RSV IMMUNIZATION This vaccination is recommended for: Adults 60 years old and over Infants and young children |